Can you be HIV-positive and test Negative?;- HIV causes AIDS and interferes with the body’s ability to fight infections. The virus can be transmitted through contact with infected blood, semen, or vaginal fluids.
Within a few weeks of HIV infection, flu-like symptoms such as fever, sore throat, and fatigue can occur. Then the disease is usually asymptomatic until it progresses to AIDS. AIDS symptoms include weight loss, fever or night sweats, fatigue, and recurrent infections.
No cure exists for AIDS, but strict adherence to antiretroviral regimens (ARVs) can dramatically slow the disease’s progress as well as prevent secondary infections and complications.
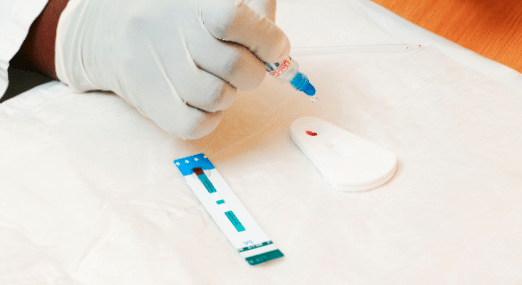
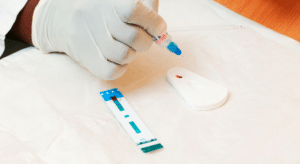
HIV tests
HIV tests are typically performed on blood or oral fluid. They may also be performed on urine. A NAT looks for the actual virus in the blood and involves drawing blood from a vein. The test can either tell if a person has HIV or tell how much virus is present in the blood (known as an HIV viral load test).
Can you be HIV-positive and test Negative?
A false negative is a test result that says a person does not have HIV when, in fact, they do. False-negative results most often occur when people test in the first few weeks after infection, during the ‘window period’ of a test. source https://www.aidsmap.com/about-hiv/false-negative-results-hiv-tests
What are the 3 tests for HIV?
There are three types of HIV diagnostic tests: nucleic acid tests (NAT), antigen/antibody tests, and antibody tests.
- NATs look for the actual virus in the blood.
- Antigen/antibody tests look for both HIV antibodies and antigens.
- Antibody tests look for antibodies to HIV in your blood or oral fluid.
Hiv